tags:
- AI_generated
- Mistral
- fundamentals
- machine_learning
- overfittingDefinition
Regularization is a set of methods for reducing overfitting in machine learning models. Typically, regularization trades a marginal decrease in training accuracy for an increase in generalizability.
Regularization encompasses a range of techniques to correct for overfitting in machine learning models. As such, regularization is a method for increasing a model’s generalizability—that is, it’s ability to produce accurate predictions on new datasets.1 Regularization provides this increased generalizability at the sake of increased training error. In other words, regularization methods typically lead to less accurate predictions on training data but more accurate predictions on test data.
Regularization differs from optimization. Essentially, the former increases model generalizability while the latter increases model training accuracy. Both are important concepts in machine learning and data science.
There are many forms of regularization. Anything in the way of a complete guide requires a much longer book-length treatment. Nevertheless, this article provides an overview of the theory necessary to understand regularization’s purpose in machine learning as well as a survey of several popular regularization techniques.
Bias-variance tradeoff
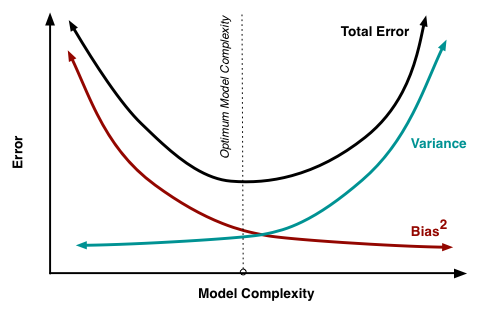
This concession of increased training error for decreased testing error is known as bias-variance tradeoff. Bias-variance tradeoff is a well-known problem in machine learning. It’s necessary to first define “bias” and “variance.” To put it briefly:
- Bias measures the average difference between predicted values and true values. As bias increases, a model predicts less accurately on a training dataset. High bias refers to high error in training.
- Variance measures the difference between predictions across various realizations of a given model. As variance increases, a model predicts less accurately on unseen data. High variance refers to high error during testing and validation.
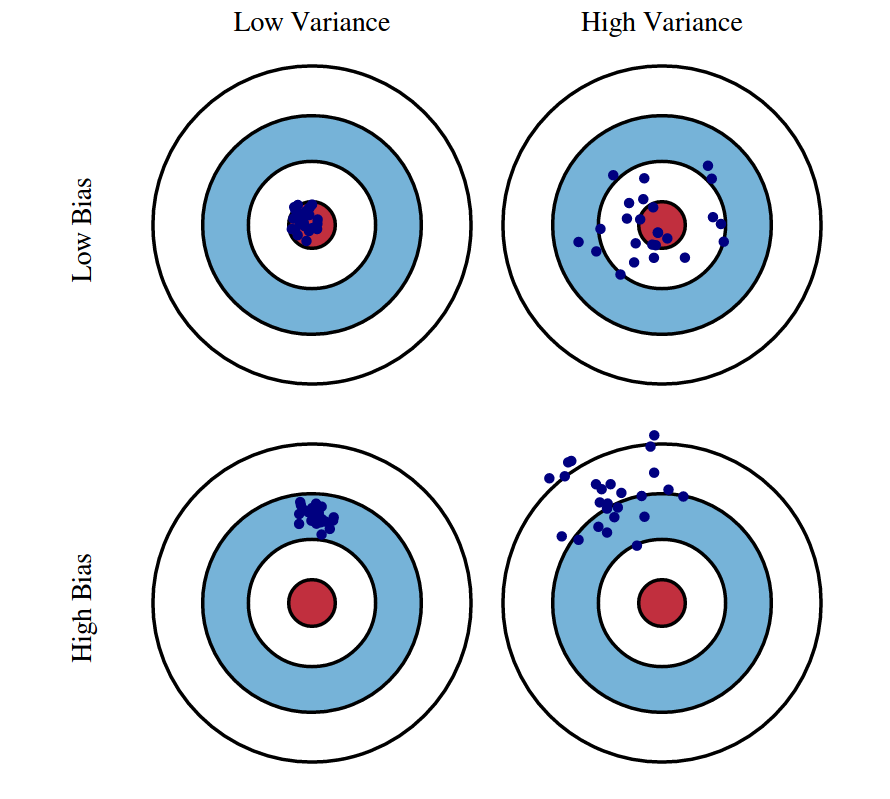
Bias and variance thus inversely represent model accuracy on training and test sets respectively. Obviously, developers aim to reduce both model bias and variance. Simultaneous reduction in both is not always possible, resulting in the need for regularization. Regularization decreases model variance at the cost of increased bias.
State-of-the-Art Regularization Techniques for FCN Architectures
Regularization techniques are essential for preventing overfitting and improving the generalization of neural networks. Here are some state-of-the-art regularization techniques that are easy to implement:
-
Dropout:
- Description: Randomly sets a fraction of input units to zero at each update during training time, which helps prevent overfitting.
- Implementation: Add a dropout layer with a specified dropout rate (e.g., 0.5) after dense layers.
-
- Description: Adds a penalty equal to the absolute value of the magnitude of coefficients to the loss function.
- Implementation: Add L1 regularization to the kernel or bias of dense layers.
-
- Description: Adds a penalty equal to the square of the magnitude of coefficients to the loss function.
- Implementation: Add L2 regularization to the kernel or bias of dense layers.
-
Early Stopping:
- Description: Stops training when the performance on a validation set starts to degrade, indicating overfitting.
- Implementation: Use a callback in Keras to monitor validation loss and stop training when it stops improving.
-
- Description: Normalizes the inputs of each layer to have a mean of zero and a variance of one, which helps stabilize and accelerate training.
- Implementation: Add a batch normalisation layer after dense layers.
-
Data Augmentation:
- Description: Generates new training samples by applying random transformations to the existing data, which helps the model generalize better.
- Implementation: Use data augmentation techniques like rotation, scaling, and flipping for image data.
-
Weight Regularization:
- Description: Applies regularization directly to the weights of the network, encouraging smaller weights.
- Implementation: Use kernel regularizers in dense layers.
-
Learning Rate Scheduling:
- Description: Adjusts the learning rate during training to improve convergence and generalization.
- Implementation: Use learning rate schedulers or adaptive learning rate optimizers like Adam.
-
Ensemble Methods:
- Description: Combines predictions from multiple models to improve performance and reduce overfitting.
- Implementation: Train multiple models with different architectures or initializations and average their predictions.
-
Noise Injection:
- Description: Adds random noise to the inputs or hidden layers during training to improve robustness.
- Implementation: Add Gaussian noise layers to the network.